
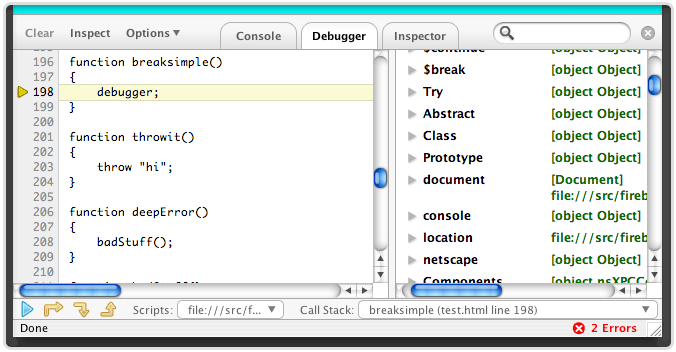
This, however, puts a burden on developers, when it comes to debugging the code in scenarios where it works fine on one browser but fails on another. Modern content management systems (CMS) such as Drupal, Joomla, WordPress, etc, empower Web development by embedding the client side code within their content entities. Initially written in 2006, Firebug went through numerous updates, making it a favourite tool for Web software developers, as it certainly makes their lives easier.

It is a free and open source plug-in with a BSD licence. Firebug is one of the most popular add-ons of Mozilla Firefox for Web development. This is especially true for runtime debugging on HTML, CSS and JavaScript tags. When it comes to browser client-side scripting that needs to be debugged, there are few tools available. It also helps in creating bug-free code that can run across leading browsers seamlessly.Īs the world of open source development evolves, debugging code is becoming a complex task. While Firebug focuses on JavaScript performance and provides detailed information about JavaScript function calls during the profiling session, the Performance Tool in the DevTools offers a broad spectrum of information regarding a website’s performance but doesn’t go into detail regarding JavaScript function calls.Here’s an introduction to Firebug, which is used primarily for debugging client side scripts in real time and reducing development time. This is the part where Firebug and the DevTools differ the most, because the outputs are completely different. it also provides information about HTML parsing or layout. The output of the Call Tree is the one that comes nearest to the output in Firebug, but the Performance panel provides much more information than just the JavaScript performance. A profile can be created via console.profile() and console.profileEnd() like in Firebug or via the “Start Recording Performance” button in the Performance Tool.

The DevTools provide advanced tooling regarding performance profiling.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
